Education is the cornerstone of personal growth and academic success, yet the learning path varies greatly depending on where in the world you find yourself. The American and British education systems stand as two pillars of excellence, each with its distinct approach to nurturing young minds. Understanding the disparities between these curricula is essential for students, parents, and educators alike, as it shapes the trajectory of academic achievement and future opportunities.
In this blog series, we delve into the nuances of the American and British curricula, exploring their structural differences, philosophical underpinnings, and educational methodologies.
Additionally, we’re excited to announce that Ignite Training Institute stands ready to offer comprehensive tutoring support tailored to both the British and American curricula. Whether you’re navigating the rigorous demands of the British curriculum’s IGCSEs and A-Levels or seeking guidance through the complexities of the American curriculum’s Advanced Placements, our expert tutors are here to provide personalized assistance and foster academic excellence.
Structure Of The American Curriculum
The structure of the American curriculum is characterized by its flexibility and emphasis on a broad-based education. While there are some commonalities across different states and school districts, the American education system allows for considerable variation in curriculum design and implementation. Here’s an overview of the typical structure of the American curriculum:
1. Elementary School (Grades K-5):
- Elementary education in the United States typically spans from kindergarten (age 5-6) through fifth grade (age 10-11).
- The curriculum at this level focuses on foundational skills such as reading, writing, mathematics, science, and social studies.
- Other subjects such as art, music, physical education, and sometimes foreign languages may also be introduced at this stage.
2. Middle School Or Junior High (Grades 6-8):
- Middle school or junior high typically encompasses grades six through eight, although the exact grade configuration can vary by school district.
- The curriculum expands upon the foundations laid in elementary school and introduces more specialized subjects.
- Core subjects continue to be emphasized, while students may also explore elective courses in areas such as technology, computer science, and foreign languages.
3. High School (Grades 9-12):
- High school in the United States typically spans grades nine through twelve, with students graduating around age 17-18.
- The high school curriculum is structured to prepare students for college, career, and beyond.
- Core subjects include English/language arts, mathematics, science, and social studies, with students often required to take a certain number of credits in each area to graduate.
- In addition to core subjects, high school students have the opportunity to choose elective courses based on their interests and career goals. These may include advanced placement (AP) courses, honors courses, vocational education, fine arts, and physical education.
- Many high schools also offer extracurricular activities, such as sports, clubs, and community service opportunities, which complement the academic curriculum.
4. Post-Secondary Education:
- After completing high school, students have the option to pursue further education at colleges, universities, technical schools, or vocational institutions.
- Post-secondary education in the United States offers a wide range of degree programs and courses of study, including bachelor’s degrees, associate degrees, certificates, and vocational training programs.
- The American higher education system is known for its diversity and flexibility, allowing students to tailor their education to their individual interests and career aspirations.
5. Courses Offered:
- English/Language Arts: Reading, writing, literature analysis, communication skills.
- Mathematics: Algebra, geometry, calculus, statistics, etc.
- Science: Biology, chemistry, physics, environmental science, etc.
- Social Studies: History, geography, civics, economics, government.
- Foreign Languages: Spanish, French, German, Mandarin, etc.
- Electives: Computer science, technology, fine arts, performing arts, physical education, health, vocational education, etc.
Overall, the American curriculum is designed to provide students with a well-rounded education that prepares them for success in an increasingly diverse and globalized world. The emphasis on flexibility allows students to explore their interests, develop critical thinking skills, and pursue their academic and career goals.
Related: What Is The Difference Between Edexcel & Cambridge? 5 Facts
Structure Of The British Curriculum
The British curriculum, often referred to as the National Curriculum, provides a structured framework for education in schools across England, Wales, Scotland, and Northern Ireland. While there are variations in implementation across these regions, the core elements of the British curriculum remain consistent. Here’s an overview of the structure of the British curriculum:
1. Early Years Foundation Stage (EYFS):
- The EYFS is the foundation stage of education for children aged 0-5 years.
- It focuses on seven areas of learning: communication and language, physical development, personal, social, and emotional development, literacy, mathematics, understanding the world, and expressive arts and design.
- The emphasis is on play-based learning, exploration, and developing key skills and concepts.
2. Key Stage 1 (KS1) & Key Stage 2 (KS2):
- Key Stage 1 covers children aged 5-7 years (Years 1 and 2), while Key Stage 2 covers ages 7-11 years (Years 3 to 6).
- The core subjects at these stages include English, mathematics, science, and computing.
- Other foundation subjects include art and design, design and technology, geography, history, music, and physical education.
- At the end of Key Stage 2, students are assessed through standardized tests known as SATs (Standard Assessment Tests) in English and mathematics.
3. Key Stage 3 (KS3):
- Key Stage 3 covers ages 11-14 years (Years 7 to 9).
- The curriculum at this stage builds upon the foundation laid in Key Stage 2 and introduces more specialized subjects and concepts.
- In addition to English, mathematics, and science, students study subjects such as history, geography, modern foreign languages, design and technology, art and design, music, drama, physical education, and citizenship.
5. Key Stage 4 (KS4) – GCSE (General Certificate of Secondary Education):
- Key Stage 4 covers ages 14-16 years (Years 10 and 11).
- The core subjects include English, mathematics, and science, with students typically taking exams leading to qualifications known as GCSEs.
- In addition to these core subjects, students choose optional subjects from a range of disciplines, including humanities, languages, arts, and vocational subjects.
- GCSEs are externally assessed through examinations, and the results are used for further education and employment opportunities.
6. Post-16 Education – A Levels (Advanced Levels) and Vocational Qualifications:
- After completing Key Stage 4, students have the option to continue their education through post-16 programs.
- A Levels are academic qualifications typically taken over two years (Years 12 and 13) and are widely recognized for entry into universities and higher education institutions.
- Alternatively, students may choose vocational qualifications, such as BTECs (Business and Technology Education Council) or apprenticeships, which provide practical skills and training for specific industries and careers.
Overall, the British curriculum is designed to provide a comprehensive and balanced education that equips students with the knowledge, skills, and qualifications needed for further study, employment, and lifelong learning. It emphasizes both academic achievement and personal development, fostering critical thinking, creativity, and adaptability.
Related: 10 Proven Strategies On How To Study For IGCSE Exams & Excel
Difference Between American And British Curriculum
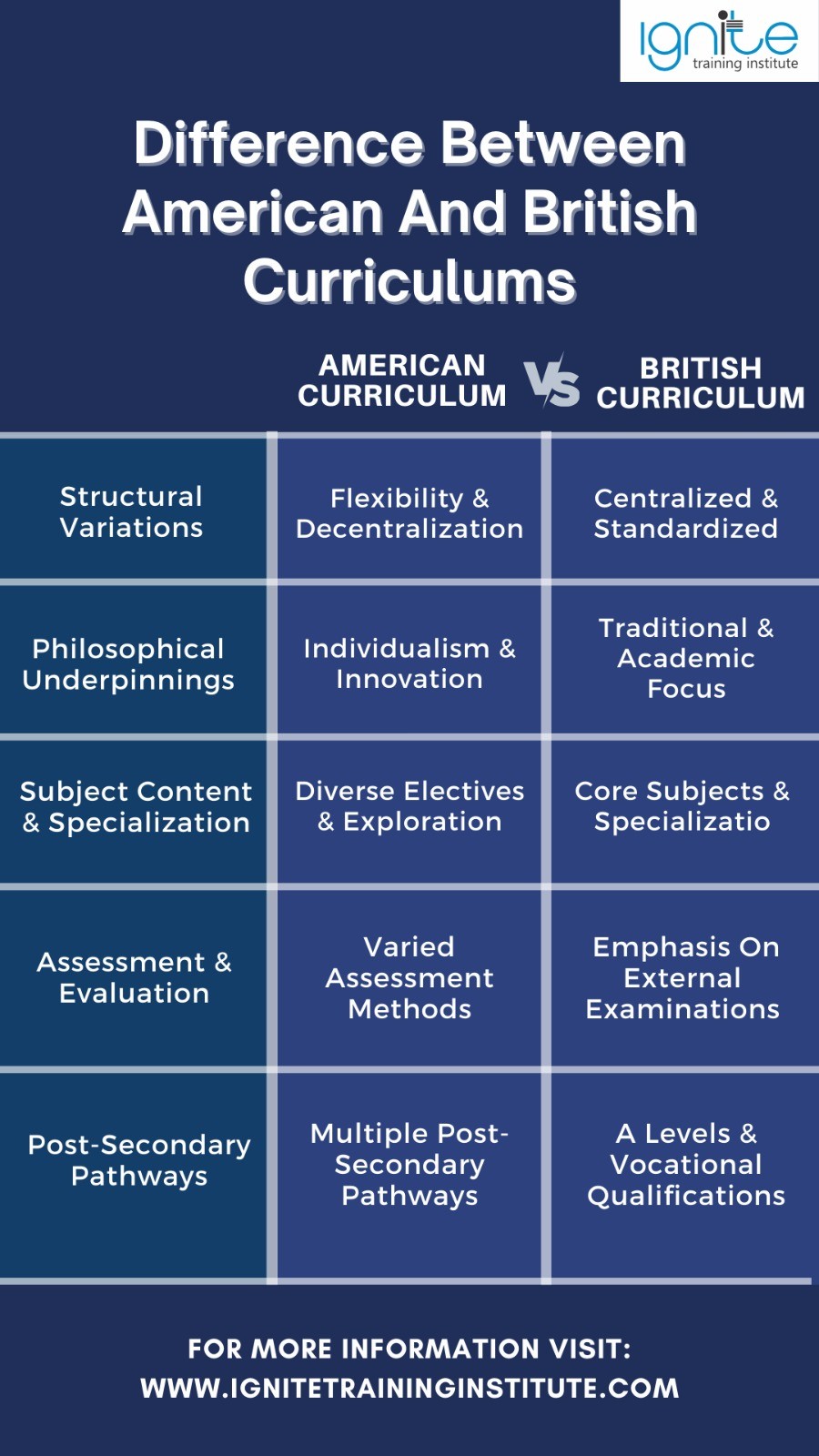
The differences between the American and British curricula stem from their unique historical, cultural, and educational philosophies. While both systems aim to provide quality education, they diverge in several key aspects. Here’s a detailed exploration of the differences between the American and British curricula:
1. Structural Variations:
American Curriculum: The American curriculum is characterized by its flexibility and decentralization. Education in the United States is primarily governed at the state and local levels, leading to variations in curriculum design and implementation across different regions.
The curriculum typically follows a K-12 structure, with elementary, middle, and high school divisions. The curriculum allows for a wide range of elective courses and extracurricular activities, providing students with opportunities to explore their interests and talents.
British Curriculum: In contrast, the British curriculum, also known as the National Curriculum, is more centralized and standardized. It provides a structured framework for education across England, Wales, Scotland, and Northern Ireland.
The curriculum is divided into key stages (from Early Years to Key Stage 5), with prescribed learning objectives and subject content for each stage. While schools have some flexibility to adapt the curriculum to their contexts, there is greater uniformity compared to the American system.
2. Philosophical Underpinnings:
American Curriculum: The American curriculum emphasizes individualism, innovation, and student-centered learning. It values critical thinking, creativity, and problem-solving skills.
Education in the United States is often viewed as a means to foster personal growth, social mobility, and entrepreneurial spirit. There is a strong emphasis on holistic development, with a focus on both academic achievement and character development.
British Curriculum: The British curriculum reflects a more traditional and academically rigorous philosophy. It places importance on knowledge acquisition, intellectual depth, and mastery of core subjects.
The curriculum emphasizes respect for authority, academic discipline, and preparation for structured pathways in higher education or employment. It aims to build a strong foundation of knowledge while fostering analytical and independent thinking within a more formalized learning structure.
3. Subject Content & Specialization:
American Curriculum: American students benefit from a broad curriculum with numerous electives in arts, sciences, humanities, technology, and vocational subjects. The system promotes interdisciplinary learning and allows for early exploration of diverse interests.
As students progress through high school, they can begin to specialize by selecting advanced courses, including AP (Advanced Placement) options that may count toward college credit.
British Curriculum: In contrast, the British curriculum places greater emphasis on core subjects and specialization in specific academic disciplines. In secondary education, students typically narrow their focus during GCSEs and later at the A-Level stage, where they select three to four subjects to study in depth.
This allows for focused academic preparation, particularly for university-bound students, and is well-suited for those with a clear career direction early on.
4. Assessment & Evaluation:
American Curriculum: Assessment in the American curriculum is often more varied and holistic, with a combination of standardized tests, teacher evaluations, project-based assessments, and portfolios.
There is a growing emphasis on competency-based assessment and performance tasks that measure real-world skills and competencies. Grading is often continuous, allowing students to improve over time and demonstrate progress holistically.
British Curriculum: Assessment in the British curriculum is more standardized and relies heavily on external examinations, such as SATs (Standard Assessment Tests) at the end of Key Stage 2 and GCSEs (General Certificate of Secondary Education) at the end of Key Stage 4.
These examinations play a significant role in determining students’ progression and qualifications.
5. Post-Secondary Pathways:
American Curriculum: The American curriculum provides multiple pathways for post-secondary education, including traditional four-year colleges, community colleges, vocational schools, and apprenticeship programs.
There is an emphasis on college readiness, and students have the option to pursue advanced placement (AP) courses and examinations for college credit.
British Curriculum: In the British curriculum, the primary pathway for post-secondary education is through A Levels (Advanced Levels) or vocational qualifications taken in the final years of secondary school.
These qualifications are widely recognized for entry into universities and higher education institutions. Additionally, there are opportunities for students to pursue vocational education and apprenticeships for practical skills training.
In summary, while both the American and British curricula aim to provide quality education, they differ in terms of structure, philosophy, subject content, assessment practices, and post-secondary pathways. These differences reflect the unique educational priorities, cultural values, and societal expectations of each country.
Related: IB Curriculum VS British Curriculum: 5 Factors To Consider
Ignite Training Institute: Tutoring Support For American & British Curriculum
Ignite Training Institute is a premier tutoring center that provides comprehensive support for students navigating the American or British curriculum. Recognizing the unique demands of each educational system, Ignite offers tailored tutoring services to ensure academic success.
For students following the American curriculum, the institute’s experienced tutors focus on personalized assistance for AP courses. Similarly, for those immersed in the British curriculum, Ignite’s tutoring support covers key stages, emphasizing core subjects and exam preparation, including GCSEs and A Levels.
With a commitment to fostering a deep understanding of subject matter and enhancing critical thinking skills, Ignite Training Institute stands as a valuable resource for students seeking excellence in their academic journey within either the American or British educational frameworks.
Related: IB VS IGCSE: The Exact Differences Between The Programs
FAQs
1. What Is The Difference Between IB, American And British Curriculum?
The International Baccalaureate (IB) curriculum offers a globally focused, inquiry-based approach to education, emphasizing international-mindedness and holistic development. In contrast, the American curriculum tends to prioritize flexibility and individualized learning, while the British curriculum often follows a more structured, subject-specific approach with standardized assessments.
2. Is The Cambridge Curriculum British Or American?
The Cambridge Curriculum is British in origin, developed by the University of Cambridge International Examinations (CIE), and follows the educational standards and frameworks established in the United Kingdom.
3. How Does The UK Differ From The American Grade System?
The UK education system typically follows a numerical year group system (e.g., Year 1, Year 2) while the American system often uses grade levels (e.g., Grade 1, Grade 2). Additionally, the UK system may include key stages to group students by age range, whereas the American system generally divides education into elementary, middle, and high school divisions.
4. What Is The Difference Between British And International Curricula?
The British curriculum, such as the National Curriculum in the UK, is standardized and tailored to specific national educational standards, while international curricula, like the International Baccalaureate (IB) or Cambridge International Examinations (CIE), offer globally-focused frameworks with an emphasis on international-mindedness and a broader range of subjects.
5. Is The British Curriculum Harder Than The American?
The British curriculum (like IGCSE and A-Levels) tends to be more specialized and exam-focused, especially in the final years. In contrast, the American system emphasizes a broader, continuous assessment approach. Neither is inherently harder, but the British curriculum is often considered more rigorous in subject depth.
6. What Is The Difference Between Education In The US And The UK?
The US education system emphasizes a broad-based curriculum with flexibility in subject choices and continuous assessments. The UK system is more structured, with students specializing earlier (e.g., A-Levels) and final exams playing a major role in academic outcomes.
7. What Is The Difference Between Indian Curriculum And American Curriculum?
The Indian curriculum (such as CBSE or ICSE) is content-heavy and exam-driven, with a strong focus on theoretical knowledge. The American curriculum, on the other hand, promotes critical thinking, extracurricular engagement, and continuous assessment, offering more flexibility in subject selection and pacing.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the disparities between the American and British curricula are not just differences in structure and content, but reflections of distinct educational philosophies and cultural values. While the American curriculum emphasizes flexibility, individualism, and a broad-based approach to learning, the British curriculum favors structure, academic rigor, and specialization.
Understanding these nuances is crucial for students, parents, and educators as they navigate the educational landscape and make informed decisions about academic pathways.
Related: Indian Curriculum VS British Curriculum: What To Consider?